Principles x of Antibody Production
The blood contains two types of white blood cell or leukocyte
Lymphocytes B cell ( produce antibodies
__________________1
Antibodies
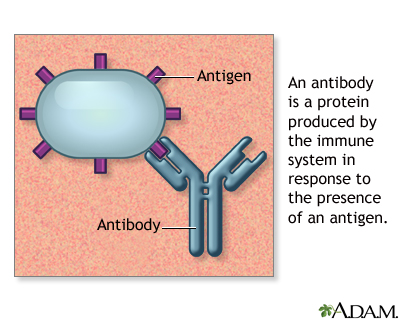
• Antibodies are proteins secreted by B cells that specifically bind to a foreign substance Antigen
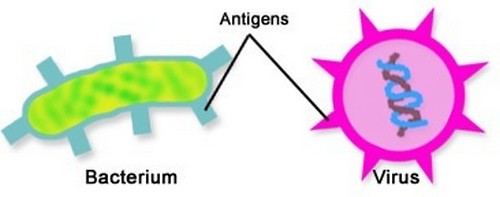
• Antigens :are foreign substances that stimulate the production of antibodies
Many of the molecules on the surface of viruses and bacteria are antigens
_____________________2
Antibodies are specific- they usually bind to only one specific antigen.
- لكل antigen جسم مضاد خاص به فقط ويرتبط معه فقط
- لان الجسم المضاد يغير مفاتيح الارتباط ( رمز الارتباط - شكله ) كي يلائم رمز او شكل الـ antigen
- antibody - نثية
- antigen - فحل
- 1- antibody = paratope
- 2- antigen = epitope
- الفحل يمرض النثية
_________________3
Production of Antibodies by Lymphocytes
A lymphocyte can produce only one type of antibody so a huge number of different types are needed
- الخلية اللمفاوية نوع B تستطيع ان تنتج اجسام مضادة من نوع واحد عند مهاجمة الكائن الدخيل الجسم
- معنى هذا ان الجسم لا يستطيع الدفاع عن نفسه اذا دخل اكثر من دخيل مختلف
- اي اصيب مثلا بكورونا وبنفس الوقت اصيب ب سارس 1
- سيكون الجسم عادة جسم مضاد خاص بكورونا لكن سارس 1 لن تتلود اجسام مضادة خاصة له
Each lymphocyte has some of its antibody on its surface...
The antigens of a pathogen bind to the antibodies in the surface membrane of a lymphocyte...
... This activates the lymphocyte.
__________________5
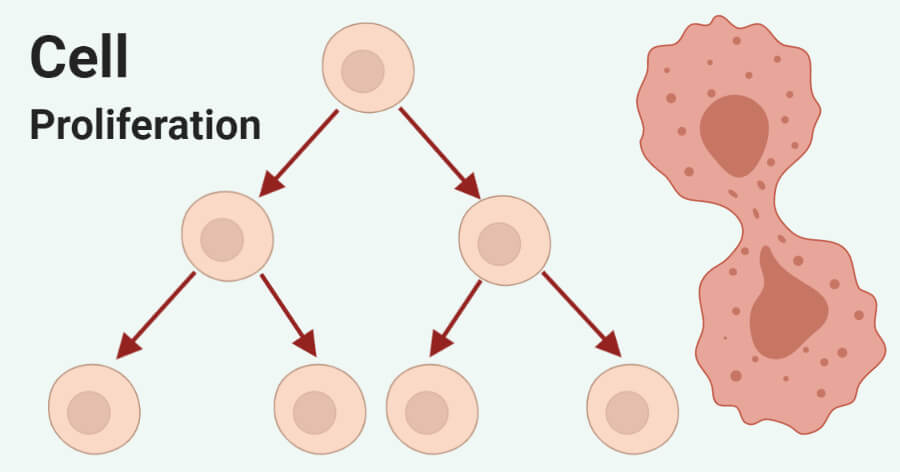
The active lymphocyte divides by mitosis to produce a clone of many identical cells
MITOSIS
The clone of cells starts to produce large quantities of the same antibody...
- clone - استنساخ : استنساخ كيلون الباب
- يعني لازم الـ paratope يطابق الـ epitope
... the same antibody needed to defend against the pathogen!
الصورة اعلاه كاملة للسلايد
_________________6
Most microbes have more than one antigen on their surface, so...
...they stimulate more than one type of lymphocyte...
...resulting in the production of many different antibodies.
These are called polyclonal antibodies.
الأجسام المضادة متعددة النسائل polyclonal antibody : هي أجسام مضادة تفرزها نسائل مختلفة من الخلايا البائية ضمن الجسم. وهذه الأجسام عبارة عن مجموعة من جزيئات الغلوبيولين المناعي تتفاعل ضد مولد ضد محدد وكل منها يتعرف على حاتمة مختلفة
____________________7
كلمات واردة في المخطط
Structure of an antibody
antigen binding site
variable constant
antigen binding site
light chain
heavy chain
________________8
What is an antibody?
- Protein secreted by B-cells that specifically bind a foreign substance (antigen)
- Immunoglobulin domains
- Immunoglobulin = antbody
- Immunoglobulin : الغلُوبولين المَناعِيّ هو بروتين على شكل حرف Y الإنكليزي ويتواجد في الدم والسوائل الجسمية الأخرى في الفقاريات، ويتم استخدامه من قبل جهاز المناعة للتعرف على الأجسام الأجنبية وتحييدها مثل البكتيريا والفيروسات
- فائدة الجسم المضاد هي التحييد وليس القتل
- CDRs = Complementarity-determining Regions
- Fab= Fragment antigen binding
- Hinge
- Fc= Fragment crystalline
- F(ab)'2= Protease digestion still useful to bind antigen
Protease : هي مجموعة من الإنزيمات البروتينية تعمل على تحلل جزيئات البروتين الكبيرة وتجزئتها إلى بروتينات قصيرة
- Protease : يشبه اللحيم في مهمته ( كبس الجسم الماضد مع المستضد )
______________9
Stages in Antibody Production
1.Antigen presentation
2.Activation of helper T-cells
3.Activation of B-cells
4.Production of plasma cells
5.Production of memory cells
________________10
Antibody Production: The Primary Response
Step 1: Antigen Presentation
Antigen
Macrophages take in antigen by endocytosis
The macrophage processes the antigen and attaches it to a membrane protein called a MHC protein
The MHC protein is moved to the cell surface membrane by exocytosis so that the antigen is displayed on its surface.
مُعَقَّدُ التَّوافُقِ النَّسيجِيِّ الكَبير- Major histocompatibility complex
سمي هذا البروتين بهذا الاسم لانه مزود بواسمات "الذاتية "، حيث ان دوره في الجسم هو تحديد ما هو ذاتي وما هو "غريب ".
- طرد الممحصين واجب = exocytosis - MHC
- عزيزي المخرج ( ecocytosis ) اعرضلي ( display ) المستضد على الغشاء السطحي الخلوي
السلايد كله
تلخيص لما ورد اعلاه
ملاحظة
- histocompatibility complex class I = MHC
- MHC = يمحص - يعني توافق نسيجي
- Enhances the destruction of infected cells by CTLs.
- prevents uninfected cells from being killed by NK cells
ملاحظة
- CTL = cytotoxic T lymphocyte - CD8
- يعني بغداد بعد اعدام صدام ادمرت بالمفخخات ( تدمير الخلية المصابة )
- CTL - الكتل بعد اعدام صدام صار ابلاش
يعني باختصار
- خلية مصابة : تقتل بواسطة CD8
- خلية غير مصابة : تنجوا بواسطة NK cell
______________10
Step 2: Activation of Helper T-cell
receptor
CD4+ : Helper T-cell
Helper T-cells have receptors on their cell surface membranes which can bind to antigens presented by macrophages.
- ماكرون ( macrophage ) يقدم نموذج صغير للمستضد الى لبنان ( T helper cells ) . وبعد ارسال النموذج سوف تتنشط لبنان T helper cells
Helper T-cell binds to macrophage presenting the antigen
Macrophage sends a signal to activate the helper T-cell
__________________11
Step 3: Activation of B-lymphocytes
B-cells have antibodies in their cell surface membranes
- لبنان ( T helper cells ) الان هي من ستقدم نموذج ال antigen الى B cells . وبعد ارتباط الـ antigen بال antibody االموجود على الغشاء السطحي لخلايا B cells سوف تتنشط خلايا B cells
Antigens bind to the antibodies in the surface membranes of B-cells
Antigen
Inactive B-cell
Antibody
_____________________12
An activated helper T-cell with receptors for the same antigen binds to the B-cell
SIGNAL
The helper T-cell sends a signal to the B-cell, activating the B-cell.
- بعد ان تعطى الاشارة تتفعل الخلية المرسل اليها الاشارة ايََ كانت
- الخلايا يجب ان تتواص مع بعضها كي تفهم بعضها البعض بان هناك مشكلة والمشكلة محصورة بـ antigen الموجود بين اطارات المستقبلات
_______________________13
التكاثر او الانتشار - Step 4: Proliferation
The activated B-cell starts to divide by mitosis to form a clone of plasma cells.
clone - استنساخ : استنساخ كيلون الباب
Plasma cells are activated B-cells with a very extensive network of rough endoplasmic reticulum.
- (plasma cells = activated B cell + rough endoplasmic (ER
- للمعلومة / الشبكة الاندوبلازمية الخشنة تكون محببة لانها تحتوي على رايبوسومات وهي مسؤولة عن ازالة السمية الموجودة سواء في الدواء او الممرض ( مولد الضد - antigen ) بالاضافة الى مشاركتها في تصنيع البروتينات والدهون والكاربوهيدرات الخ ...
Plasma cells synthesis large amounts of antibody, which they excrete by exocytosis.
______________14
The Secondary Response: Memory Cells
• If an antigen invades your body a second time, a much faster response occurs which produces much larger quantity of the required antibody.
•When activated B-cells are dividing during the primary response, some cells stop dividing and secreting antibody and become memory cells.
س\ ما الفرق بين الاصابة الاولى والاصابة الثانية ؟
- ج\ في الاصابة الاولى يتطلب انتاج اجسام مضادة كافية لمواجهة الممرض كثير من الوقت حوالي ( 7- 15 يوم ) , حيث تنقسم الخلايا البائية عدة انقسامات لكي تتدارك الممرض وتعرف نوعه ومدى وحشيته
- الاصابة الثانية تتطلب فيها عملية انتاج الاجاسم المضادة وقت قصير لانه في الاصابة الاولى عندما تنقسم الخلايا البائية فان معضم تلك الانقسامات تتحول الى اجسام مضادة بينما خلايا تائية محدودة تتوقف عن استمرارية الانقسام وتتحول الى ذاكرة بحيث تكون مهمة مواجهة الممرض اسهل واسرع واكثر كفائة ايضا
• Large numbers of memory cells remain in the body for a long time...
....they are capable of producing large amounts of antibody very quickly when stimulated.
______________________15
Antibody Production: Summary
Summary - ملخص - الحضارة السومرية لخصت معنى الشجاعة
____________________17
Principles of antibody production
- . Clonal selection
1015antibodies < -
B-cells clone themselves -
- Challenge and response
- Immunity developed only when disease challenges the immune system
ماهي مبادء انتاج الاجسام المضادة
1- مبدأ الاختيار
2- مبدأ التحدي + مبدأ الاستجابة
- مبدأ اختيار النسيلة
- انتاج اكثر من 1015 جسم مضاد | يعني 10 متبوعة ب 15 صفر (كوادريليوم )
- استنساخ الخلايا البائية نفسها ( الخلية الواحدة تعطي خليتين ..الخ )
2. مبدأ التحدي والاستجابة
- يفشل الجهاز المناعي في تحدي ( مواجهة ) العامل الممرض عندما يتغلب الممرض على جهاز المناعة اي ( يتحدى ) هو الاخر جهاز المناعة كما في الايدز وغيره
ملاحظة فرق ببين
- clonal - نسيلة
- clone - نسخ
_______________________20
Antigen dependent maturation of B cells
Activation phase: B cell proliferation and differentiation
Recognition phase :
كلمات واردة في الصورة
Resting mature B cell
Clonal expansion : التوسع النسيلي هو العملية التي تنشأ من خلالها الخلايا الوليدة من الخلية الأم. أثناء التوسع النسيلي للخلية البائية ، يتم إنتاج العديد من النسخ من تلك الخلية البائية التي تشترك في التقارب مع نفس المستضد وخصوصياته
IgG-expressing B cell
Isotype switching : التأشيب البدالي الصنفي : هي آلية البيولوجية التي يتغير بموجبها إنتاج الأضداد ( الاجسام المضادة ) من قبل الخلية البائية من صنف معين إلى آخر مثل تحول نمط الكلوبين المناعي من igM الى اكلوبين مناعي اخر مثل igG
High-affinity Ig expressing 8 cell
Affinity maturation - نضج متقارب ( متشابه )
-High affinity IgG
Phases of the humoral immune response.
Memory B cell
لاحظ ان الخلايا البائية عندما تستمر بالانقسام تعطي
1- خلايا بلازمية - ثم اجسام مضادة من نوع ( igM ) متصلة
2- خلايا بائية معبرة من نوع igG تعطي بدورها( خلايا بلازمة + اجسام مضادة ) منفصلة ( isotype switching )
3- خلايا بائية معبرة عالية التشابه تكون على نوعين
4- النوع الاول ينقسم فيعطي ( خلية ابلازمية + اجسام مضادة ) iffinity maturtion
5- النوع الثاني لا ينقسم فيعطي خلايا الذاكرة memory B cell
____________________21
معاني
- Activates complement- ينشط المكمل
- Placenta transfert - الانتقال المشيمي : في النساء الحوامل، قد تعبر الأجسام المضادة من نوع igG لمرض الذئبة المشيمة إلى الجنين. ونتيجة لذلك، قد يكون لدى الجنين معدل ضربات قلب بطيء جدًا أو فقر الدم أو انخفاض في عدد الصفائح الدموية أو انخفاض في عدد خلايا الدم البيضاء. ومع ذلك، تختفي هذه الأجسام المضادة تدريجيًا على مدى عدة أسابيع بعد ولادة الطفل، وتزول المشكلات التي تسببها باستثناء بطء معدل ضربات القلب.
- mast - بدينة - البدينة تمسي على حبيبها
- opsonization - طهي مناعي ( له علاقة بالبلعمة )
- allergic - التحسس - رج البطل يسبب حساسية
انواع الأجسام المضادة
تقوم هذه الأجسام بالدفاع عن الجسم ضد البكتيريا والفيروسات، وتوجد في مختلف سوائل الجسم، حيث أنها الأصغر حجمًا، وبالتالي تتحرك بسهولة في الخلايا.
2. الأجسام المضادة (IgM) - العجم اول من استجاب لنداء الاستغاثة العراقية
تعد الأكبر حجمًا بين الأجسام المضادة( حجم قاسم سليماني كبير )، وتوجد في المخاط والدموع واللعاب والدم، بالإضافة إلى بعض المناطق الأخرى من الجسم.
وتنتج هذه الأجسام استجابةً للعدوى الفيروسية ( ال اسعود ) أو البكتيرية ( الصهاينة )، وتقوم بمنع الأعداء من إصابة الخلايا بضرر، كما أنه تحول دون وصولها للأعضاء الداخلية ( الاراضي الايرانية ) .
3. الأجسام المضادة (IgE)
تقوم هذه الأجسام برد فعل تجاه المواد المثيرة للحساسية، سواء الأتربة والغبار، أو الفطريات، أو الأطعمة المسببة للحساسية، وكذلك تحمي الجسم من الديدان الطفيلية.
4. الأجسام المضادة (IgA) - اجة المنبطح - حيدر العبادي
توجد هذه الأجسام بنسبة كبيرة في الأغشية المخاطية، وخاصةً في بطانة ممرات التنفس والجهاز الهضمي، كما تتوفر في الدموع واللعاب.
وتعمل هذه الأجسام ( حيدر العبادي - igA على منع دخول الأجسام الغريبة والضارة ( داعش ) إلى داخل الدورة الدموية .
5. الأجسام المضادة (IgD) - لم اجد مستقبل
هي النوع الأقل نسبة بالجسم، وتوجد بكميات صغيرة في الدم، وعادةً ما تكون موجودة مع الأجسام المضادة (IgM) على شكل مستقبلات لخلايا B ، يعني ( D.M - دم ) وتقوم بتعزيز نشاط خلايا المناعة.
___________________22
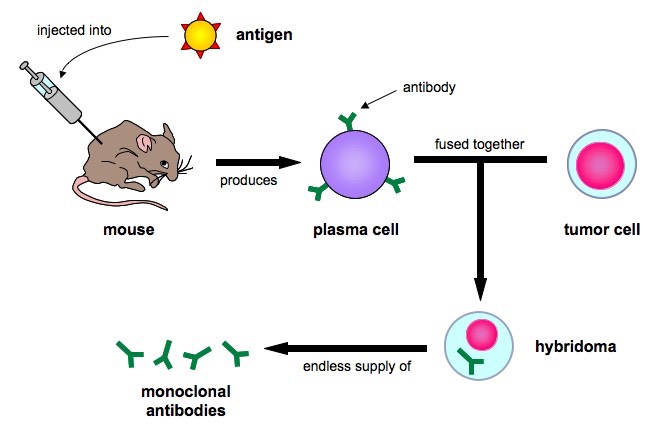
Production of monoclonal antibodies
1. Antigens injected to an animal
2. B-cells extracted from the animal
3. Tumour cells obtained
4. B-cells fused with tumour cells
antigen binding sites
5. Hybridoma cells- produce antibody
6. Antibodies are extracted and purified
يعني ببساطة
- احقن الـ antigen داخل حيوان ( فئرة مثلا )
- سيقوم الجسم بانتاج خلايا ابلازمية لمواجهة مولد الضد , فاقوم باستخراج هذه الخلايا البلازمية B cell ) من الفئر
- نحصل على خلايا سرطانية من مصدر خارجي ( ليس من نفس الفئر )
- اخلط ( اهجن ) الخلايا البلازمية ( B cell ) مع الخلايا السرطانية داخل الفئر ( في موقع ارتباط الـ ( antigen )
- الخلايا المهجنة المخلوطة ( Hybridoma cells ) ستنتج اجسام مضادة احادية النسيلة ( monoclonal antibody )
- استخرج الـ monoclonal antibody واقوم بتنقيته
____________________23
Monoclonal Antibody Production
- Monoclonal Antibody Production technology was developed in 1975. Since its development it has been very important in the modern medical science with the diagnosis, therapy, research and even basic science today. It is still largely dependent upon animal testing however. Because it requires immunization of mice in order for them to create the antibodies to be grown.
فرق بين
1- polyclonal - اجسام مضادة لها اشكال مختلفة
2- monoclonal - اجسام مضادة لها شكل واحد
- . Monoclonal Antibody Production or mAb is produced by cell lines or clones obtained from the immunized animals with the substance to be studied. Cell lines are produced by fusing B cells from the immunized animal with myeloma cells. To produce the desired mAb, the cells must be grown in either of two ways: by injection into the peritoneal cavity of a suitably prepared mouse (the in vivo, or mouse ascites, method) or by in vitro tissue culture.
myeloma cell : هو مرض سرطاني يصيب الخلايا البلازمية من نوع B مما يؤدي إلى تكاثر هذه الخلايا بشكل غير طبيعي وتكدسها في نخاع العظم.
- The vitro tissue culture is the method used when the cells are places in culture outside the mouse's body in a flask.
__________________24
Monoclonal Antibody Production
Immunization
Tumor cells
Antibody-forming cells
Fusion
Tissue culture
Hybridomas
Hybidromas screened for antibody production
Antibody-producing hybridomas cloned
Monoclonal antibodies isolated for cultivation
__________________25
Why this method is used!!
- This method is used because antibodies must be formed from the immunization of the substance being studied. So antibodies must be produced. Once the antibodies are produced the animal aspect of the study can be eliminated and tissue culture can then be used.
- . When using live mice researchers have found that it is the better option because in vitro doesn't always produce adequate cell lines that are adaptive to tissue culture. Protein denaturation can occur from purification techniques and antibody activity is decreased with normal activity not represented. Also cell lines could possibly become contaminated when using in vitro technique.
__________________26
Polyclonal antibodies:
If an animal is immunized with a protein, a wide array of B cells will be stimulated to produce anti-protein antibodies.
Antibodies may be made to a number of different epitopes of the protein.
Even antibodies that bind to the same epitope may have different antigen-binding sites and bind the epitope with different affinity.
The mixture of antibodies produced in response to an antigen are referred to as polyclonal antibodies (they are produced by many different clones of B cells).
mixture of antibodies = polyclonal antibodies
________________27
Producing polyclonal antibodies
الفرق بين الـ polyclonal و monoclonal
1- monoclonal : يؤخذ الجسم المضاد من حيوان واحد
2- polyclonal : يؤخذ من عدة حيوانات مختلفة
كلمات واردةpolyclonal antibodies containing taken out from the animals bodies
Base on the read of the amount of anabodies select animal based on their
antigen
Secreted antibodies
Polydonat arabodes from different B-cesare produced
________________________28
MONOCLONAL VS POLYCLONAL ANTIBODIES
MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES
- Expensive to produce
- Training is required for the technology used
- Time scale is long for hybridization
- Can produce large amount of specific antibodies.
- Recognizes only 1 epitope on an antigen
- Once hybridoma is made it is a constant and renewable source. No or low batch to batch variability.
POLYCLONAL ANTIBODIES
Active and passive immunity
- Active immunity: antibodies by the organism itself
- Passive immunity: antibodies received from another organism
- During pregnancy antibodies passed to the fetus
active = antigen
passive = antibody
_______________________30
Antigenic determinants
- An antibody will recognize
- Epitope: defined segment of an antigen -
Immunoreactivity of epitopes may depend on primary -
secondary, tertiary or quaternary structure of an antigen
النشاط المناعي من epitopes يعتمد على
- primary ( توبة اوليية )
- secondary ( توبة ثانوية )
- tertiary ( توبة ثالثية )
- quaternary ( توبة رباعية )
Define the possible applications -
Variability of epitopes depends on the species -
- Antibodies are antigen themselves
________________________30
Commercial production of antibodies: polyclonal vs monoclonal
- Host animals ca be used to raise antibodies against a given antigen
- Slected clones from a polyclonal each recognizing a single epitope can be fused to a tumor cell (hybridoma) to proliferate indefinitely
Monoclonal Antibody Production
السلايد بالكامل
Laboratory use of antibodies
- . Quantitation of an antigen
RIA, Elisa -
المقايسة المناعية الشعاعية - RIA : هي تقنية فحص حساسة جداً في المختبر مستخدمة لقياس تراكيز المستضدات عن طريق استخدام أجسام مضادة.
- Identification and characterization of protein antigens
Immunoprecipitation -
Western blotting -
- Cell surface labelling and separation
- Localisation of antigens within tissues or cells
- . Expression librairies
- Phage display
____________________32
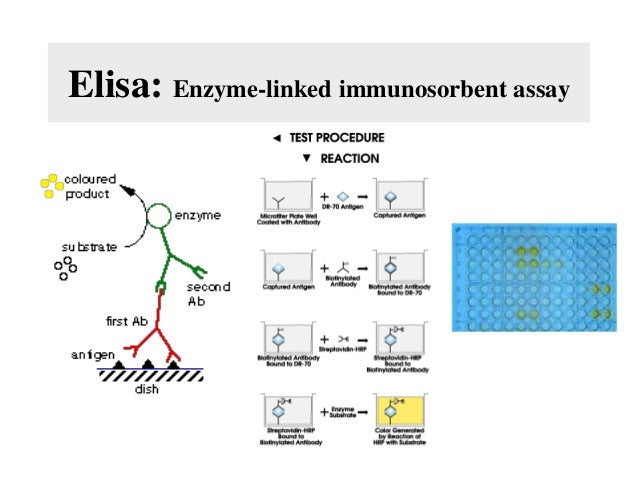
Elisa: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
مقايسة الممتز المناعي المرتبط بالإنزيم - elisa : هي اختبار كيميائي حيوي يعتمد على استعمال الأجسام المضادة، والتغيير اللوني، في التعرف على وجود مادة-مستضد عادةً- في عينة ما
شرح مبسط لتقنية الايلازا
كلمات واردة
TEST PROCEDURE
▾ REACTION
coloured product
enzyme
Captured Antigen
substrate
0%
DR-70 Agen
Microffer Plate Wel
Coated with Antibody
second Ab
first Ab
anigen
Abody
Bound to DR-70
dish
Biotykated Antibody
Captured Antigen
Abody omyloted Antibody Bound to DR-10
Antibody
Color Generated by eaction of
___________________33
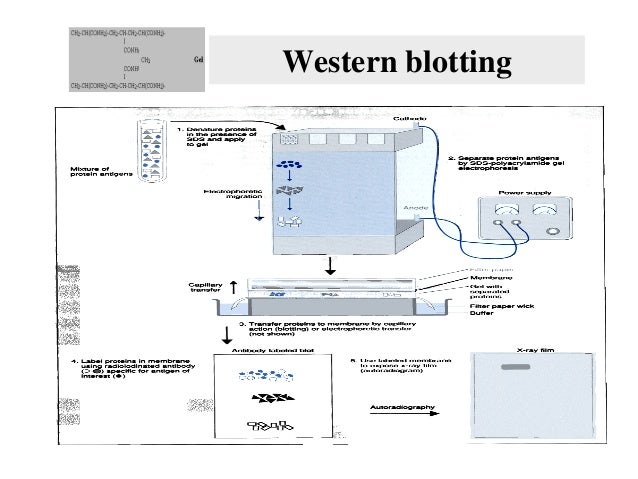
Western blotting
كما واردة
Gel
CONH
Cathode
1. Denatura proteine to
Mixture of protein antigens
2. Separate protein angens by SDS-patyworytamede gel electrophoresin
Power supply
Capillary
Membrane
-Gat with
3. Transfer proteins to membrane by capillary melon (blotting) or electrophoretic transfer
4 Label proteine in membrane using radiolodinated antibody specife for antigen of interest (
Antibody-labeled to
5. Use labele membrane
Autoradiography
X-ray film
____________________33
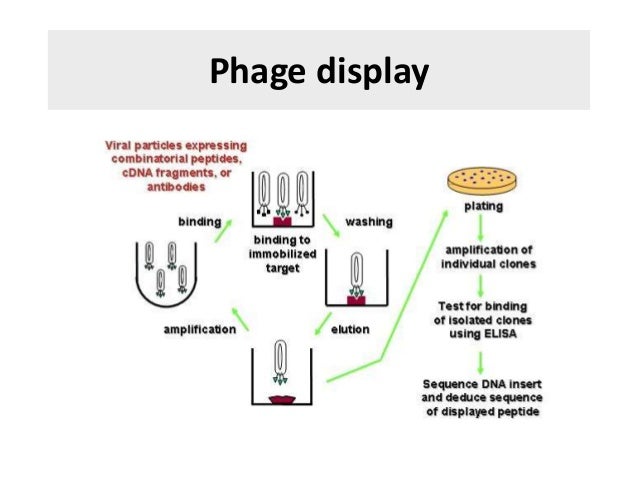
Phage display
Viral particles expressing combinatorial peptides, cDNA fragments, or antibodies
binding
amplification
binding to immobilized target
elution
washing
plating👇
amplification of individual clones👇
Test for binding of isolated clones using ELISA👇
Sequence DNA insert and deduce sequence of displayed
_________________________34
Clinical use of antibodies
1. Diagnostic
- Detection of peptides and other molecules in various - diseases
- Endocrine diseases: hyperinsulinemia, diabetes, hyperparatyroidism
- Tumor antigens (p53 tumor suppressor, PSA, a-foetoprotein)
- Antibodies against viral proteins (AIDS, hepatitis)
Therapeutic .2
- - Neutralizing antibodies
- • Anti-ErbB2 for breast and ovarian cancer
- • Anti-CD20 for B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
- • Antisera and antidotes (viruses and venoms)
3. Drug discovery
- - Identification of therapeutic targets (phage display)
________________________35
Physiological roles of antibodies
- Protect against
- - Viral infections
- - Bacterial infections
- - Foreign bodies Antigens
2. Deleterious in
- - Autoimmune diseases
- . Reumathoid arthritis Lupus
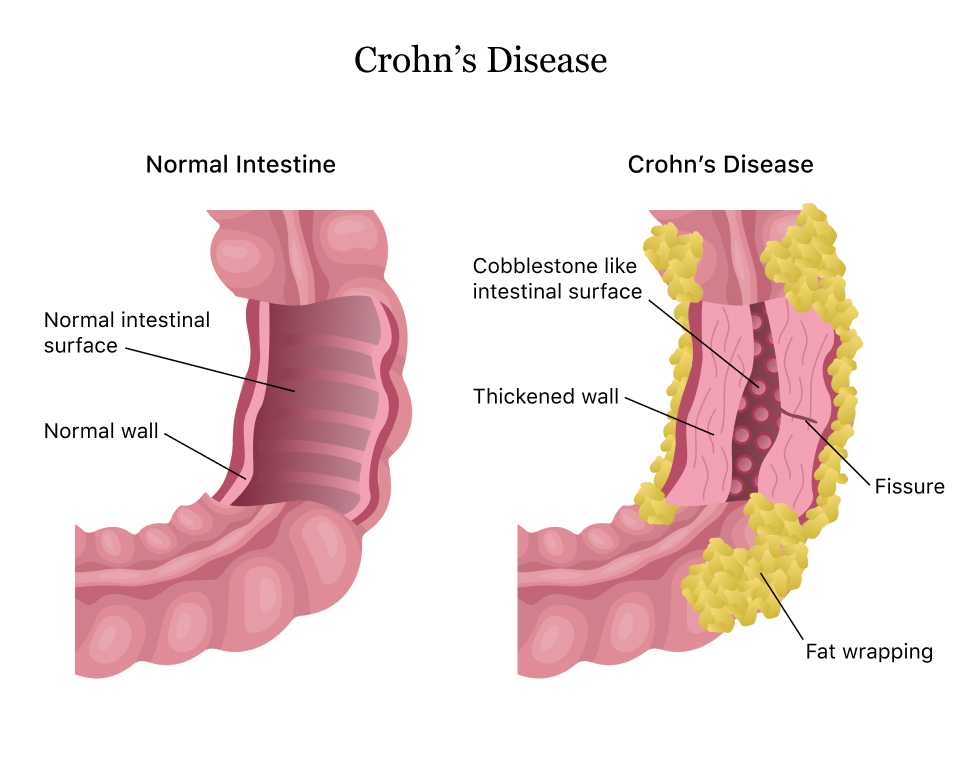
- . Type 1 diabetes Croh'n disease
- Lupus
Croh'n disease
- - Graft rejection and hypersensitivity responses
السايد كامل













































تعليقات
إرسال تعليق